cost to install manual transfer switch
Summary
Find out the average cost to install a manual transfer switch, including detailed pricing and factors affecting installation expenses.

A manual transfer switch enables safe connection of a generator to a home’s electrical system during outages, ensuring reliable power supply while avoiding hazards like back-feeding.
1.1 What is a Manual Transfer Switch?
A manual transfer switch is a device that enables safe switching between two power sources, such as a grid and a generator. It acts as a secondary fuse box, directing power to specific circuits in a home. This setup prevents back-feeding and ensures safe, efficient energy distribution during outages. The switch is crucial for maintaining electrical safety and reliability in residential setups, especially during emergencies.
1.2 Importance of a Manual Transfer Switch for Home Generators
A manual transfer switch is vital for safely connecting a generator to a home’s electrical system during power outages. It prevents dangerous back-feeding to the grid and ensures reliable energy distribution. The switch provides flexibility, allowing homeowners to control which circuits receive generator power. This not only enhances safety but also offers a cost-effective solution compared to automatic switches. It’s an essential component for maintaining electrical integrity and preventing hazards, making it a critical investment for generator owners.

Average Cost to Install a Manual Transfer Switch
The average cost to install a manual transfer switch ranges from $1,200 to $1,600, with an average of $1,450, depending on materials and labor.
2.1 Materials Cost
The materials cost for a manual transfer switch installation includes the switch itself, wiring, conduit, and connectors. A 30-amp switch costs around $200, while a 200-amp model can range up to $1,000. Additional materials like circuit breakers, transfer panels, and weatherproof enclosures add to the expense, potentially increasing the total materials cost to $1,500 or more, depending on the system’s complexity and brand quality.
2.2 Labor Cost
Labor costs for installing a manual transfer switch vary based on the electrician’s hourly rate and the job’s complexity. On average, labor costs range from $300 to $1,200. Licensed electricians typically charge $75 to $150 per hour, and the installation may take 2 to 8 hours, depending on the system’s size and setup. Factors like remote locations or complex wiring can increase labor expenses, ensuring the job is done safely and correctly.
2.3 Total Average Cost
The total average cost to install a manual transfer switch ranges from $800 to $2,700, depending on materials and labor. Materials typically cost $500 to $1,500, while labor ranges from $300 to $1,200. The average total cost is around $1,200 to $1,600 for a standard installation. Factors such as the size of the transfer switch, installation complexity, and location can influence the final price. Hiring a licensed electrician ensures compliance with safety standards and local regulations.

Factors Affecting the Cost of Installation
The cost to install a manual transfer switch is influenced by the switch’s size, type, location, and local electrical codes, impacting both materials and labor expenses.
3.1 Size and Capacity of the Transfer Switch
The size and capacity of the transfer switch significantly impact installation costs. A larger switch with higher amp ratings requires more materials and labor, increasing expenses. For instance, a 200-amp transfer switch costs more than a 100-amp one due to the heavier-duty components needed. Additionally, the number of circuits supported by the switch influences the price, as more circuits require additional wiring and circuit breakers. Electricians often assess the electrical load requirements to determine the appropriate size, ensuring reliable performance during power outages while adhering to safety standards.
3.2 Type of Transfer Switch (Manual vs. Automatic)
The type of transfer switch significantly impacts installation costs. Manual switches are generally more affordable and simpler to install, with fewer components. Automatic switches, while more convenient, are pricier due to their complex mechanisms and additional features, such as sensors to detect power outages. Labor costs also rise with automatic switches, as they require more advanced setup and programming. The choice between manual and automatic depends on budget, desired convenience, and specific electrical needs, influencing overall installation expenses.
3.3 Location and Accessibility
The location and accessibility of the transfer switch significantly influence installation costs. Installing the switch near the main electrical panel reduces labor time and expenses. Conversely, remote or hard-to-reach locations increase labor costs due to additional time and materials required. Outdoor installations may also necessitate weatherproofing, further adding to the expense. Easy access ensures faster and more cost-effective installation, while complex or inaccessible locations can complicate the process, driving up overall costs and labor efforts.
3.4 Local Electrical Codes and Regulations
Local electrical codes and regulations play a crucial role in determining installation costs. Compliance with codes may require specific materials or additional safety measures, increasing expenses. Permits and inspections mandated by local authorities also add to the cost. Non-compliance can lead to fines or rework, further escalating costs. Electricians must adhere to these regulations, ensuring the system is safe and legally approved. This adherence, while necessary, contributes to higher overall installation expenses for homeowners seeking a manual transfer switch setup.

Components of a Manual Transfer Switch System
A manual transfer switch system includes a transfer switch panel, inlet, outlet, and wiring. These components ensure safe power distribution from the generator to the home’s circuits.
4.1 Transfer Switch Panel
The transfer switch panel is the core component, acting as a secondary fuse box. It safely connects the generator to the home’s electrical system, distributing power to selected circuits. Pre-wired with labeled wires and flexible conduit, it simplifies installation. The panel ensures safe power delivery, preventing back-feeding and electrical hazards. It typically includes circuit breakers or fuses for overload protection. Compatibility with generator power inlet and home wiring is crucial for reliable operation during outages.
4.2 Inlet and Outlet
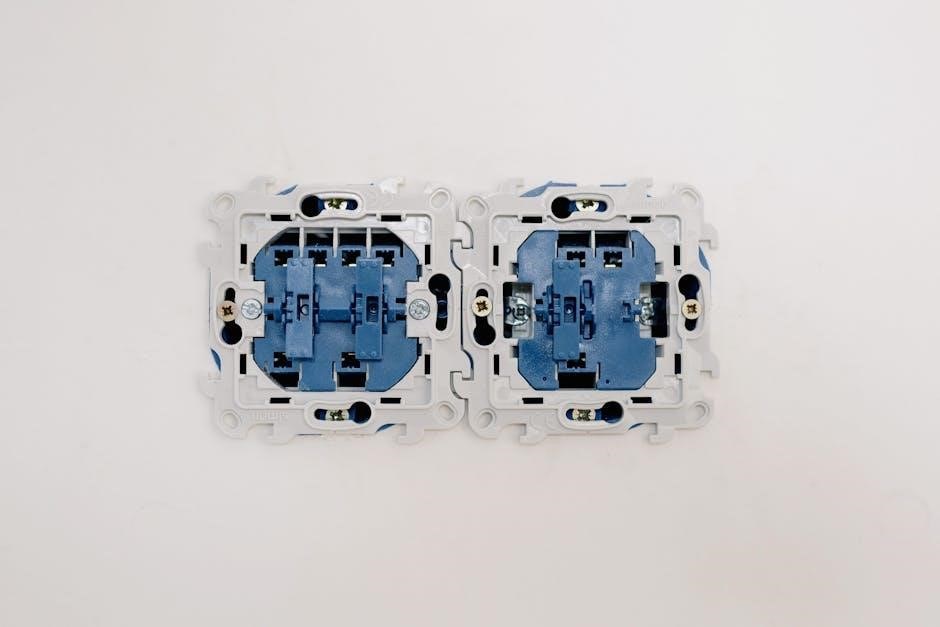
The inlet and outlet are critical ports on the transfer switch panel. The inlet connects to the generator, typically via an L14-30 power inlet, ensuring safe power delivery. The outlet distributes this power to the home’s circuits. Proper installation near the main electrical panel simplifies the process and ensures compliance with safety codes. The inlet and outlet must be correctly sized to handle the generator’s maximum load, preventing overheating and ensuring reliable backup power during outages.
4.3 Wiring and Circuit Breakers
Proper wiring and circuit breakers are essential for safe and efficient power transfer. The switch is prewired with labeled wires, simplifying installation. Flexible conduit and connectors ensure secure connections. Circuit breakers protect against overloads and short circuits, safeguarding the system and home.
Incorrect wiring can lead to hazards, making professional installation crucial. Ensuring all components are correctly sized and connected is vital for reliable backup power during outages, maintaining safety and efficiency.

Steps Involved in the Installation Process
Assess electrical needs, select the right transfer switch, install physically, and conduct thorough testing to ensure safe and efficient power transfer during outages.
5.1 Assessing Electrical Needs
Assessing electrical needs is crucial to determine the correct size and capacity of the manual transfer switch. This step involves identifying the total power requirements of the home, prioritizing essential circuits, and ensuring the switch can handle the maximum load during an outage. It also includes evaluating the generator’s capacity and compatibility with the electrical system. Proper assessment ensures efficient power distribution and prevents overload risks, making it a foundational step for safe and reliable installation.
5.2 Selecting the Right Transfer Switch
Selecting the right transfer switch involves matching its capacity with your generator and home electrical needs. Consider the number of circuits you want to power and whether you need a manual or automatic switch. The switch must be compatible with your generator’s power output and voltage rating. Additionally, ensure it meets local electrical codes and regulations. Consulting with a licensed electrician can help you choose the most suitable option for your system, ensuring safety and reliability during power outages.
5.3 Physical Installation
Physical installation involves mounting the transfer switch near the main electrical panel or generator. The electrician connects the switch to the generator inlet and the home’s electrical system. Wiring is run between the switch and the main panel, ensuring all connections are secure and meet safety standards. The process requires careful planning to avoid errors, as improper installation can lead to hazards. Typically, this step takes several hours, depending on the system’s complexity and the electrician’s experience.
5.4 Testing and Safety Checks
After installation, thorough testing ensures the system operates correctly. This includes verifying proper power transfer, checking for short circuits, and ensuring all safety features function. Testing under load simulates real outage conditions, confirming the switch handles the full power demand safely. Safety checks also verify proper grounding and compliance with electrical codes, ensuring the system is hazard-free and reliable for future use.

Safety Considerations
Safety is paramount when installing a manual transfer switch to prevent hazards like back-feeding and electrical shocks. Proper installation ensures compliance with local codes and regulations.
6.1 Why Safety is Critical
Safety is crucial when dealing with manual transfer switches to prevent electrical hazards like shocks, fires, and back-feeding. Improper installation can lead to dangerous situations, making adherence to safety protocols essential. Ensuring compliance with local electrical codes and regulations minimizes risks. Professional installation is often recommended to guarantee safety standards are met, protecting both the home and its occupants from potential electrical dangers associated with generator usage during outages.
6;2 Common Hazards to Avoid
Common hazards include back-feeding, which can damage utility grids and harm workers, and electrical shocks from improper connections. Fires may result from overloaded circuits or faulty wiring. Additionally, improper grounding or insufficient capacity can lead to dangerous conditions. Ensuring compliance with electrical codes and proper installation practices is critical to avoiding these risks and ensuring safe operation of the manual transfer switch during power outages.

DIY vs. Professional Installation
DIY installation saves money but risks safety and code violations, while hiring a licensed electrician ensures compliance and reliability, though at a higher cost.
7.1 Pros and Cons of DIY Installation
DIY installation can save money but poses risks like electrical hazards and code violations. It requires technical knowledge and tools, with potential for errors. While cost-effective for those with experience, it may lead to unsafe setups or legal issues if not done correctly. Proper wiring and compliance with local regulations are critical, making it challenging for inexperienced individuals. The complexity of the process often outweighs the savings, especially for larger systems.
7.2 Benefits of Hiring a Licensed Electrician
Hiring a licensed electrician ensures a safe and compliant installation, adhering to local codes and regulations. Professionals handle complex wiring, reducing fire hazards and ensuring proper functionality. They provide warranties and guarantees, offering peace of mind. Electricians also optimize the system for efficiency and reliability, saving time and potential future repairs. Their expertise minimizes risks associated with improper installations, making it a worthwhile investment for long-term safety and performance.
Installing a manual transfer switch is a critical investment for home generator systems, ensuring safety and reliability during power outages while adhering to electrical standards.
8.1 Summary of Key Points
A manual transfer switch is a critical component for safely connecting generators to home electrical systems during outages. The average installation cost ranges from $1,200 to $1,600, depending on materials, labor, and local regulations. Key factors influencing cost include switch size, type, location, and compliance with electrical codes. Hiring a licensed electrician ensures proper installation, safety, and adherence to standards. This investment enhances reliability and safety, making it a worthwhile addition for homeowners with generators.

8.2 Final Thoughts on Cost and Importance
Installing a manual transfer switch is a vital investment for homeowners seeking reliable backup power during outages. While the average cost ranges from $1,200 to $1,600, the benefits far outweigh the expense. It ensures safety, prevents electrical hazards, and provides peace of mind. Prioritizing professional installation guarantees compliance with safety standards and optimal performance. This upfront cost is a small price for the security and convenience it offers, making it an essential upgrade for generator owners.